
Implant Bone Grafting
Implant bone grafting is a dental procedure performed to enhance the stability and success of dental implant placement when a patient has inadequate bone density or volume in the jawbone. Insufficient bone can hinder the proper integration of dental implants, affecting their stability and long-term viability. By performing an implant bone graft, additional bone material is introduced to the deficient areas, creating a stronger and more supportive foundation for the dental implants.
Lack of height or width of the bone might have been caused by:
- missing teeth – with no teeth in the bone the tissue is not stimulated and therefore bone absorption accrues over time.
- Trauma – any incident causing bone loss.
- periodontal Disease or infection that affected the bone mass.
- Genetics – simply being born with that specific jaw bone anatomy.
Ridge Augmentation (Bone grafting, Guided bone regeneration)
Ridge Augmentation, also known as bone grafting or guided bone regeneration, plays a crucial role in the success of dental implants. Insufficient bone and tissue thickness in the jaw can lead to ridge deformities, making it challenging to achieve an esthetically pleasing dental implant restoration. These defects can result from various factors such as trauma, developmental issues, periodontal disease, or prolonged denture use.
When teeth have been missing for an extended period, the ridge undergoes shrinkage in both height and width. In severe cases, the ridge may lack the necessary width and height to accommodate a dental implant. To address this, a bone graft is performed to augment the ridge’s height and/or width, creating a solid foundation for the implant. This involves placing grafting material to enhance the surrounding bone and provide optimal support for the implant. Following a sufficient healing period, typically lasting 6-8 months, the implants can be placed in a subsequent surgical procedure.
Ridge Expansion
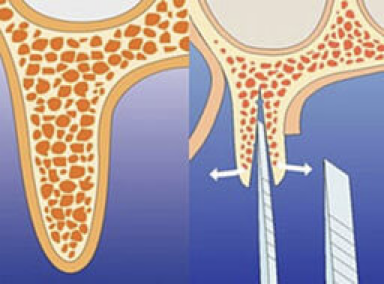
Ridge Expansion is a dental technique employed to address a thin jaw ridge that lacks the necessary dimensions for dental implant placement. This procedure involves mechanically expanding the bony ridge to restore its lost width. During the implant placement process, the jaw’s bony ridge is physically expanded using mechanical instruments.
Ridge expansion can be supplemented with the placement of bone graft material to enhance the ridge’s thickness around the implant. However, it’s important to note that this technique primarily focuses on increasing the width of the bony ridge and is not effective for increasing its height. The aim of ridge expansion is to create a more suitable foundation to support dental implants and ensure their long-term stability.
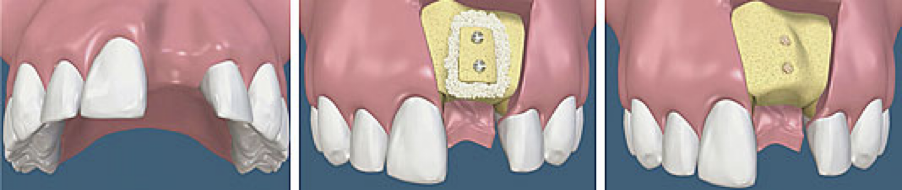
Socket Preservation
A socket is the name for the area in the bone in which a tooth is rooted.
Socket preservation is a dental procedure performed to prevent the collapse of the socket, which is the area in the bone where a tooth is rooted. When a tooth is lost or extracted, the soft tissue and bone surrounding the socket can deteriorate over time. This can lead to accelerated bone loss and potential negative effects on adjacent teeth.
To maintain both oral health and aesthetics, it is crucial to rebuild the socket promptly after tooth loss or extraction. Ridge or socket preservation surgery is conducted to prevent the collapse of this area and create a suitable foundation for tooth replacement through implant or bridge restoration. By preserving the socket, the surrounding bone and soft tissue are maintained, providing a stable and healthy environment for future dental procedures.
Overview of the implant bone grafting process
comprehensive dental examination, including X-rays or other imaging techniques, is conducted to assess the condition of the jawbone and determine the need for bone grafting. The dentist or oral surgeon evaluates the quality and quantity of available bone and identifies areas that require augmentation.
Bone Grafting Procedure: The actual bone grafting procedure typically involves the following step:
1. Anesthesia: Local anesthesia is administered to ensure your comfort during the procedure.
2. Incision and Access: The dentist or oral surgeon makes a small incision in the gum tissue to access the jawbone.
3. Bone Graft Placement: Grafting material, such as synthetic bone grafts, bone from another part of your body, or processed bone graft material, is placed in the targeted areas that need augmentation.
4. Graft Integration: Over time, the graft material integrates with the existing bone, stimulating the growth of new bone cells and blood vessels through a process called osseointegration.
5. Healing and Integration: It usually takes several months for the bone graft to fully heal and integrate with the existing bone. During this period, following post-operative instructions provided by your dentist or oral surgeon is essential for proper healing.
There are 3 typical types of bone graft material to be used:
- Autogenous bone grafting refers to the use of the patient’s own bone for dental procedures, typically sourced from other areas within the mouth such as the chin, ramus, or tuberosity. During the preparation of the implant site, the dentist collects this bone by drilling into the designated area. In rare instances, bone may be harvested from external areas outside the mouth, such as the hip, but this procedure is typically conducted in a hospital setting.By utilizing the patient’s own bone, the graft has a better chance of integrating with the existing bone, promoting natural healing and long-term stability.
- Alloplast – synthetic bone. While using this type the dentist mixes in the patient’s blood to help the material accelerate and promote bone formation in the graft area.
- Xenograft – bone taken from cow. This bone is harvested under very strict supervision and it is very safe.
After applying the bone grafting materials, a collagenmembrane is placed to hold the material in place. The membrane holds the material in place preventing soft tissue to blend in, enabling the material to regenerate and form new bone. This type of grafting material has very good result for sinus grafting procedure.
